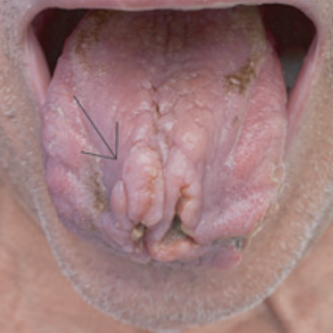
Histoplasmosis is a fungal infection endemic to areas of Central America and Midwest USA. Most people develop a mild form of infection and are asymptomatic; if symptoms do occur they are usually flu-like, but can vary greatly. In a few, usually immunosuppressed, patients the disease can progress to life-threatening, disseminated histoplasmosis. Dr Thais Pincelli and colleagues recently reviewed all 10 cases of oropharyngeal histoplasmosis identified over a 21 year period at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota.
Histoplasmosis is a fungal infection endemic to areas of Central America and Midwest USA. Most people develop a mild form of infection and are asymptomatic; if symptoms do occur they are mainly flu-like, but can vary greatly. In a few, usually immunosuppressed, patients the disease can progress to life-threatening, disseminated histoplasmosis. Dr Thais Pincelli and colleagues recently reviewed all 10 cases of oropharyngeal histoplasmosis identified over a 21 year period at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota.
In the study group, 40% were immunosuppressed and 50% had a history of heavy tobacco use – there was only one healthy non-smoker. 80% were male and 90% were thought to have disseminated histoplasmosis. Despite more than half being assessed by specialists, the median delay to diagnosis was 5 months.
Key points:
- Oropharyngeal involvement is rarely seen in immunocompromised patients and should be considered a manifestation of disseminated disease
- Common symptoms included weight loss, weakness, and oropharyngeal pain
- Tissue biopsy with fungal-specific staining is key to diagnosis – many specialists did not perform tissue biopsies, and if they did, did not send them for fungal stains or culture
Prompt initiation of antifungal treatment for disseminated histoplasmosis is essential, as it may improve patient survival and reduce morbidity. The authors state that “Any patient living in a Histoplasma endemic region who presents with painful, persistent solitary or multiple oropharyngeal ulcerations or lesions that do not resolve within 4 weeks should be sent to a dermatologist or an oral specialist for a biopsy for histological examination and fungal stains and culture.”
Read the paper: Pincelli et al (2019) Oropharyngeal histoplasmosis: a report of ten cases. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2019 Feb 1